what are you looking for?
In the search for sustainable energy solutions, solar power has emerged as a frontrunner, offering a clean and renewable alternative to traditional energy sources. Two primary configurations of solar power systems are standalone and grid-tied. Each system has its unique set of advantages and disadvantages, catering to different users and environmental conditions.
Standalone solar systems, also known as off-grid systems, operate independently of the utility grid. These systems are ideal for remote locations where grid connection is either impractical or impossible. They typically include solar panels, batteries for energy storage, a charge controller to regulate the flow of electricity, and an inverter to convert DC power to AC for household use. The key advantage of standalone systems is their self-sufficiency, providing uninterrupted power supply even during grid outages. However, the initial coasts of setting up a standalone system is usually higher due to the need for energy storage solutions.
On the other hand, gird-tied solar systems are connected to the utility grid. They do not require batteries for energy storage, as excess electricity generated can be fed back into the grid, often earning credits for the homeowner. This setup is more cost-effective initially, as it eliminates the need for battery banks. Grid-tied systems also simpler in design and maintenance. However, they are dependent on the grid for backup power, which means during a grid outage, the system will not function unless equipped with a battery backup or a grid-interactive inverter.
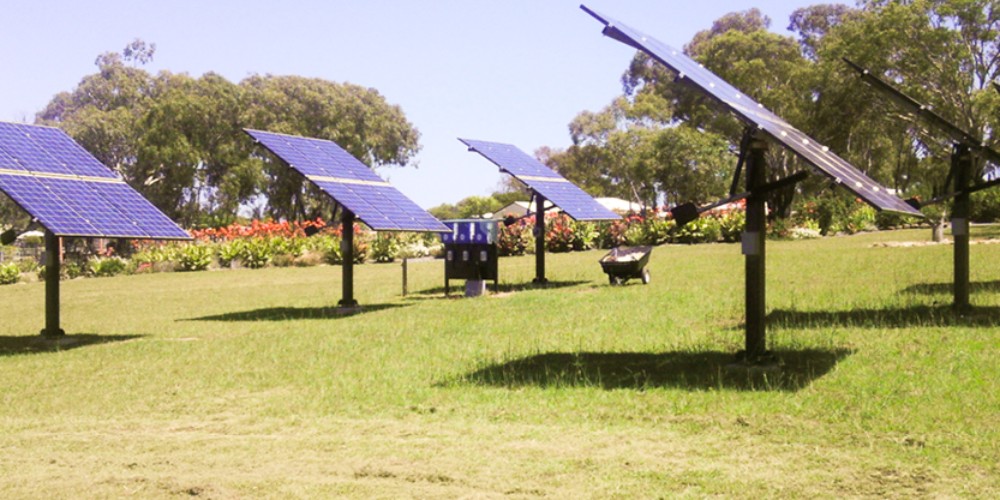

Both systems contribute positively to the environment by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. However, the environmental impact of manufacturing, transporting, and maintaining the components, especially batteries in standalone systems, should be considered. Grid-tied systems, by sharing the energy load with the grid, can reduce the overall carbon footprint associated with energy production and distribution.
The decision between a standalone and a grid-tied solar system should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of individual requirements, financial considerations, and environmental impact. As the world moves towards greater adoption of renewable energy, understanding the nuances of these systems will be important for making informed choices that align with both personal and global sustainability goals.

Xiamen SLD Technology Co., Ltd
 Chengyi North Street, Software Park 3, Jimei District, Xiamen Fujian, China
Chengyi North Street, Software Park 3, Jimei District, Xiamen Fujian, China +86 188 5929 8629
+86 188 5929 8629 sales@solarlightsdo.com
sales@solarlightsdo.com Blog | Sitemap | XML | Privacy Policy
Blog | Sitemap | XML | Privacy Policy