what are you looking for?
Solar irradiance, often referred to as solar radiation, is the amount of radiant energy emitted by the sun that reaches the earth’s surface. This energy is the driving force behind solar power generation and plays a crucial role in understanding the potential for harnessing solar energy. Measured in watts per square meter, solar irradiance is influences by various factors such as the earth’s distance from the sun, time of day, season, weather conditions, and the presence of atmosphere particles.
The intensity of solar irradiance varies throughout the day and across different geographical locations due to factors like the angle of sunlight, cloud cover, and atmospheric conditions. The angle at which sunlight strikes the earth’s surface affects the amount of energy absorbed, with peak irradiance occurring when the sun is directly overhead. Cloud cover can significantly reduce solar irradiance levels by blocking or reflecting sunlight, while atmospheric particles can scatter and absorb solar radiation.
Solar irradiance is a critical factor in determining the efficiency and performance of solar energy systems, such as solar panels and solar thermal collectors. Understanding the expected levels of solar irradiance at a specific location is essential for designing efficient solar power systems ans accurately predicting energy production. By analyzing historical solar irradiance data and considering local weather patterns, engineers and designers can optimize the placements and orientation of solar panels to maximize energy capture.
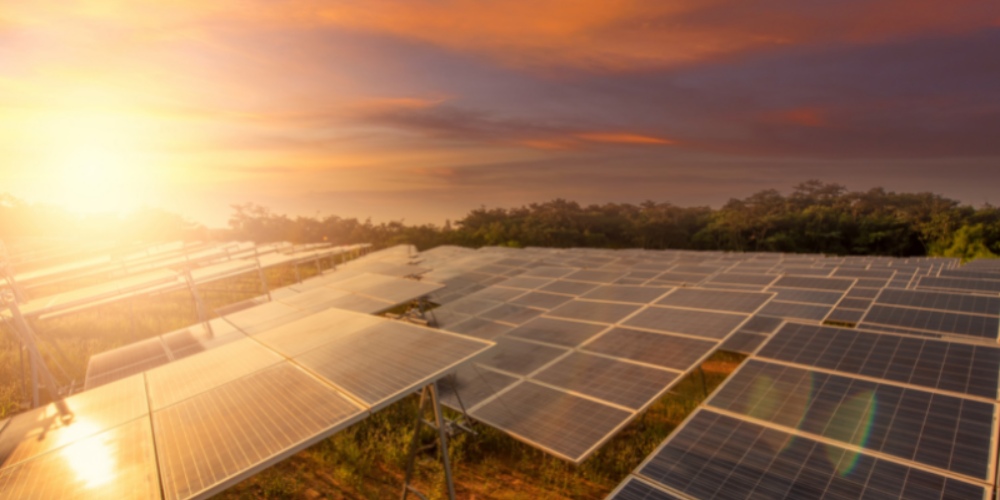

Solar irradiance is measured using devices called pyranometers, which quantify the solar energy received per unit area. These instruments are calibrated to provide accurate measurements of solar irradiance under different conditions. Additionally, satellite-based measurements and weather stations contribute to collecting data on solar irradiance levels worldwide, enabling researchers to study long-term trends and variations in solar radiation.
Advancements in technology and the increasing adoption of solar energy have driven research into improving the accuracy of solar irradiance forecasts and enhancing the efficiency of solar power systems. Innovations such as AI-powered forecasting models, smart solar tracking systems, and bifacial solar panels aim to optimize energy production by leveraging solar irradiance data. As the world transitions towards sustainable energy sources, a deeper understanding of solar irradiance will continue to drive innovations int the solar energy sector.

Xiamen SLD Technology Co., Ltd
 Chengyi North Street, Software Park 3, Jimei District, Xiamen Fujian, China
Chengyi North Street, Software Park 3, Jimei District, Xiamen Fujian, China +86 188 5929 8629
+86 188 5929 8629 sales@solarlightsdo.com
sales@solarlightsdo.com Blog | Sitemap | XML | Privacy Policy
Blog | Sitemap | XML | Privacy Policy